Metatarsalgia – what does this mean?
Metatarsalgia is an umbrella term that is used to describe ball of foot pain. Many different conditions can result in pain in this location. The metatarsals are long bones in the foot that are designed to allow an even weight distribution during walking. When this balance is disrupted, overload occurs, resulting in ball of foot pain.
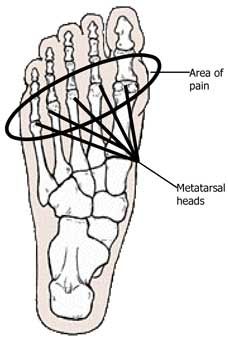
What conditions cause ball of foot pain?
Metatarsalgia can be classified as primary or secondary metatarsalgia.
Primary Metatarsalgia
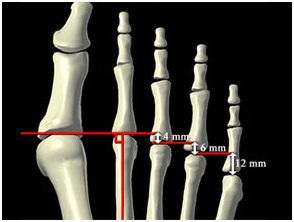
Ball of foot pain occurs in this situation due to altered biomechanics of the 1st metatarsal. Excessive weight transfer occurs through the lesser metatarsals (smaller toes) resulting in overload pain.
Examples of primary metatarsalgia include:
- Hallux Valgus (Bunion)
- Hallux Rigidus (Arthritis of 1st MTP joint – Big toe)
Secondary Metatarsalgia
This group includes specific conditions that can affect this region of the foot resulting in pain.
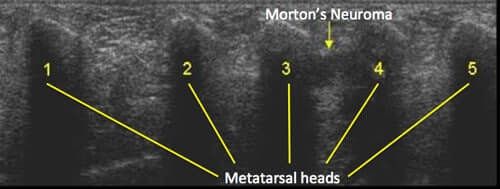
Mortons Neuroma
A morton’s neuroma is a painful condition that affects the ball of your foot. It is a painful enlargement / thickening of the nerve that supplies sensation to the skin between your toes. Most commonly these occur in the 2nd and 3rd webspaces of the foot. Classically people describe the sensation of walking with a pebble in their shoe. Nerve irritation can cause a tingling sensation, numbness, or burning.
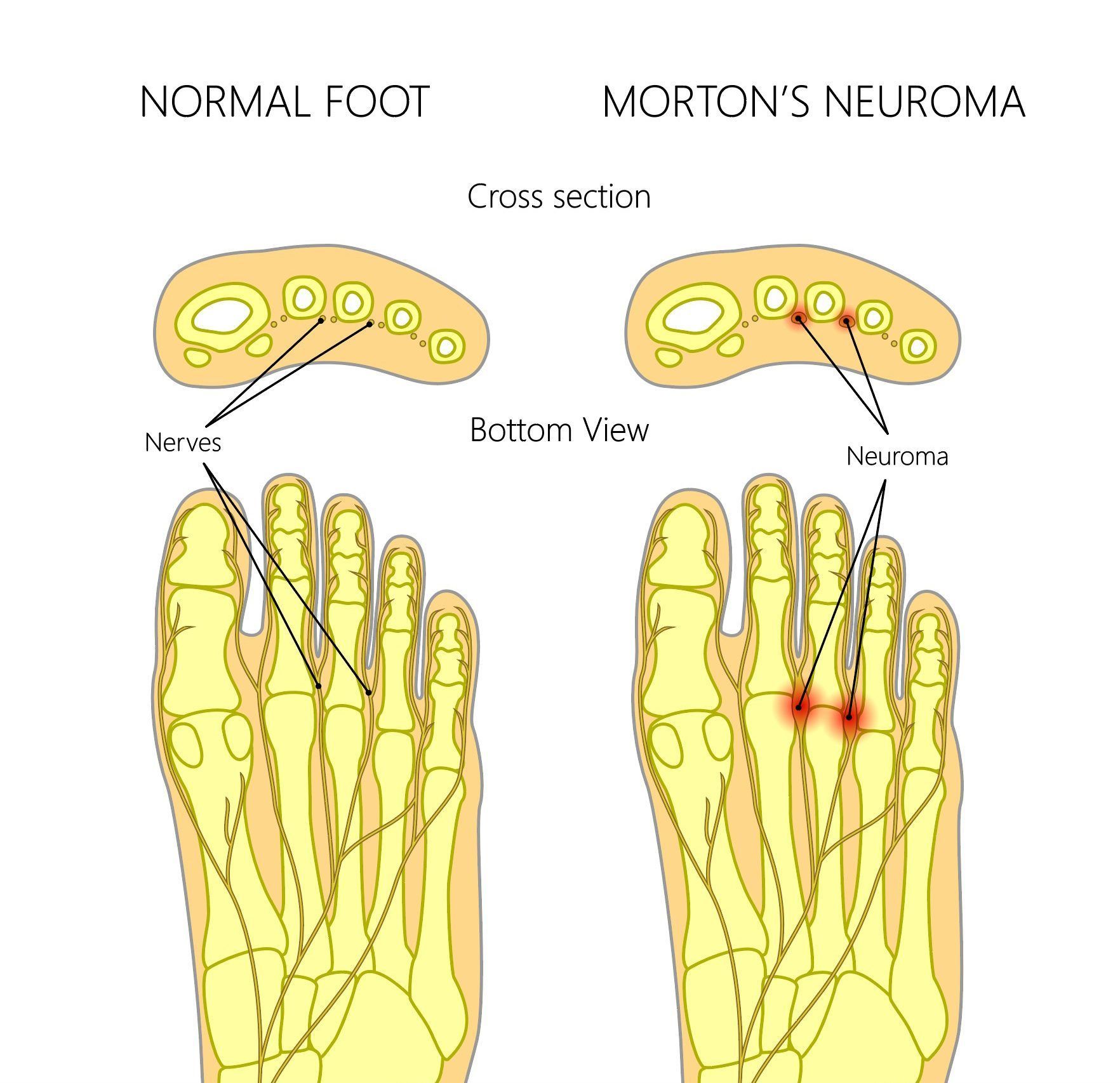
The diagnosis is confirmed clinically with a compression squeeze test, and on ultrasound.
MTP joint Bursitis
A bursa is a ‘sac like’ structure that is found in many locations in the body. When the bursa becomes inflamed, this results in bursitis. Bursal inflammation between the metatarsals can result in ball of foot pain.
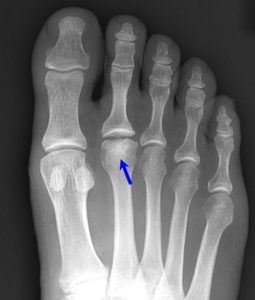
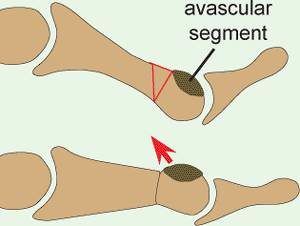
Freibergs disease
Freiberg’s disease is an uncommon condition that results in collapse of the joint surface. It most commonly affects the 2nd metatarsal head, although can also affect the other toes. It most commonly affects young to middle aged females, resulting in pain, swelling, and stiffness of the affected MTP joint.
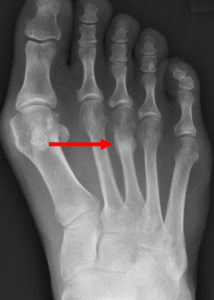
Stress Fracture
Stress fractures occur during periods of overload or a recent change in activities (i.e taking up long distance running) . The most common site of a stress fracture in the foot is the metatarsal bones. Depending on the location, most stress fractures will heal without surgery. A period of ‘rest’ and, or immobilisation, may be required.
Ball of foot pain – Making the Diagnosis
Dr Smith will conduct a thorough history to determine what is the likely cause for your ball of foot pain. As outlined above, there are many causes that need to be considered, and each of these has a different treatment plan. A detailed examination of your foot will assess for the exact location of your tenderness, determine the likelihood of you having a neuroma, and assess whether the function of your great toe is contributing to your pain.
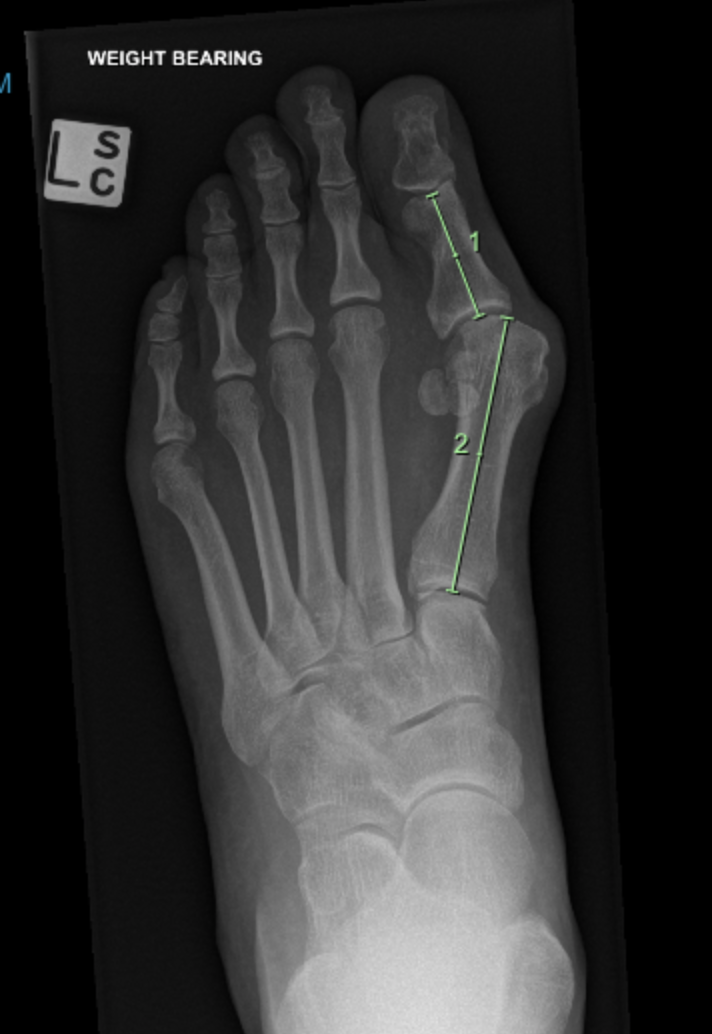
Plain weight bearing x-rays are performed to check for arthritis, stress fractures, Freiberg’s disease, and the relationship of your metatarsals (foot bones).
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, a treatment plan is initiated.
Ball of foot pain – Treatment
The treatment of your pain will depend upon your exact diagnosis.
Primary Metatarsalgia
Patients with an arthritic great toe, or bunion, may need to have these managed as part of their treatment plan.
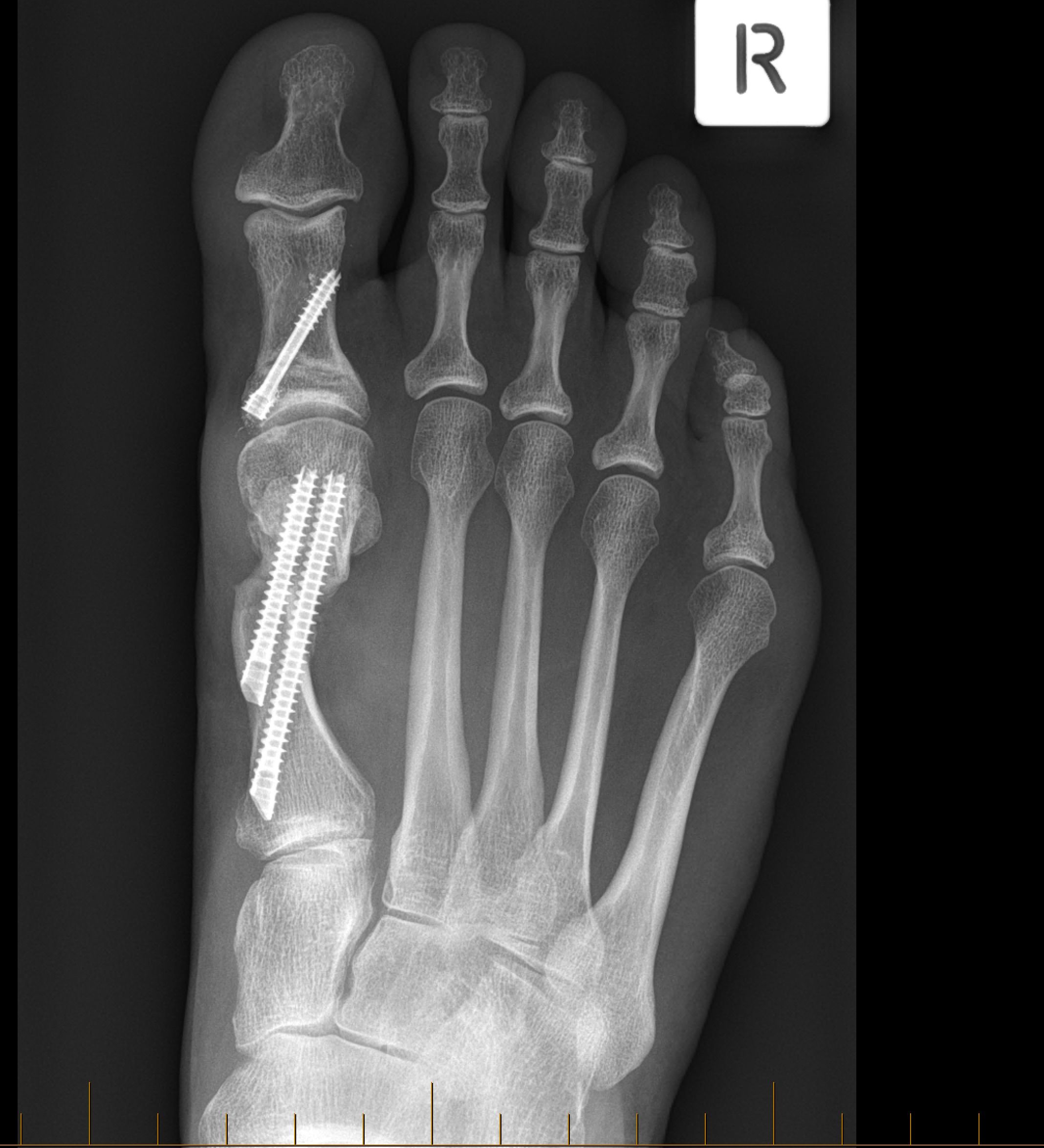
Patients with abnormal biomechanics due to excessively long metatarsal bones, may need to have a shortening osteotomy performed to unload the forces passing through the ball of the foot.
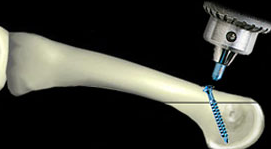
Secondary Metatarsalgia
Generic treatment options for ball of foot pain include offloading orthoses, pre-metatarsal pads, and stretching exercises. If ongoing pain is an issue, then further intervention may be required.
Mortons Neuroma
Ultrasound guided corticosteroid injections, or Radiofrequency ablation, can be considered in the management of Morton’s neuroma. If ongoing pain persists, a day surgical excision of the neuroma may be required.
MTP joint Bursitis
Ultrasound guided corticosteroid injections can be considered in the management of intermetatarsal bursitis. It is uncommon to require surgery for isolated bursitis.
Freibergs disease
Freiberg’s disease is a difficult condition to treat. Surgical options include a joint ‘debridement’ to remove the inflamed joint lining, and any loose bodies that are entrapped in the joint. Off loading osteotomies (cutting the bone) can be performed to improve the joint articulation.
Stress Fracture
The majority of stress fractures of the metatarsals can be managed conservatively. Once the diagnosis has been made, offloading the affected bone with a period of rest will often result in successful union.
Metatarsalgia Treatment
Generic treatment options for ball of foot pain include offloading orthoses, pre-metatarsal pads, and stretching exercises. If ongoing pain is an issue, then further intervention may be required. Targeted ultrasound guided steroid injections also play a role.
Is your ball of foot pain continuing to bother you?
Difficulty walking
Pain under your foot
Feels like your walking on stones

